Open Source and Closed Source Examination Technology
Source code is the technical blueprint that tells computer software how to function. When a program is released, it can either be closed source or open source. The choice is not always apparent as each option has its particularities with a mix of advantages and disadvantages.
This article will explain what closed source software and open source software are - what the difference is between them, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and finally, shed some light on why we, Digiexam, choose to walk the path of closed source in our student application to offer a secure lockdown during exams.
What is Open Source?
Open source software (OSS) refers to distributed applications with source code made freely available. They may be redistributed, copied, deleted, and modified by other users and organizations according to the restrictions set by the author. As a result, the code can be continuously updated, improved, and expanded as more people can contribute to it.
Open source software is closely related to Free Software where the user has the freedom to:
- Run the program as you wish, for any purpose
- Study how the program works, and modify it according to your computing needs
- Redistribute copies so you can help others
- Distribute copies of your modified versions to others
Examples of open source software include Firefox, OpenOffice, Gimp, Android, PHP, Perl, etc.
Advantages
- Tends to be free or inexpensive
- Anyone can add to the source code
- The user can modify the software to fit their needs
- Public collaboration is utilized to fix bugs, add features, and improve performance within a short amount of time
- Full transparency into how the application works
Disadvantages
- It may be more difficult to find technical support for less popular software
- As the code is free to edit by anyone, people may misuse the code for their gain
- It may include hidden costs such as implementation costs if you’re having trouble implementing the software yourself
- When free to use, the user is liable for the usage of the application
What is Closed Source?
Closed source software (CSS) is the complete opposite of open source software. CSS uses proprietary and protected code which is closed to the public. Only the original creator or organization can access, copy, and modify the software. Users need to have a valid and authenticated license to use the software.
Examples of closed source software include Skype, Adobe Flash, Microsoft Windows, Microsoft Office, WinRAR, Mac OS, etc.
Advantages
- The source code is protected, where only the author or organization may alter the code
- The author or organization is responsible if anything happens to the software
- Support is provided by the developers of the software
- Tight collaboration with the vendor to develop new features
Disadvantages
- Requires a valid license to use the software
- Users are not able to modify or improve the software according to their needs
Why Digiexam’s exam platform is closed source
Academic dishonesty - cheating - is one of the biggest challenges in the examination lifecycle. As costly pen and paper exams have become obsolete and inaccessible, new investments in examination technology are essential for institutions. However, many have experienced real frustrations with the new examination technology available, especially regarding security and reliability.
At Digiexam, we made a choice over a decade ago to focus on closed source technology to offer a platform with the highest possible security and reliability together with offering a scalable and accessible solution for exams. Because, our customers can’t have any hick-ups during their most important exams when there is a lot at stake and the tension is already high among students and test-takers.
What our closed source technology also provides and what we take great pride in, is that we have full ownership of the lockdown technology and are independent. This means that we have 100% liability towards the product and our customers, which results in great partnerships, where institutions can turn directly to us and have one counterpart for all matters related to the platform.
The closed source lockdown technology enables Digiexam to build a highly secure and reliable platform that works equally well in BYOD as managed environments. Furthermore customers can expect zero maintenance and no hidden costs in comparison to other technologies.
Our recommendation no matter what vendor or technology your institution chooses, make sure to check how the vendor will support you in different scenarios and what liability it has.
Comparison - Exam solutions
Sprung from higher education. Built out of Sweden. Over a decade of experience. Digiexam is an all-in-one examination platform - closed source of course - designed to safely and reliably power your whole examination lifecycle. Let’s compare the Digiexam platform and an open source lock-down exam browser:
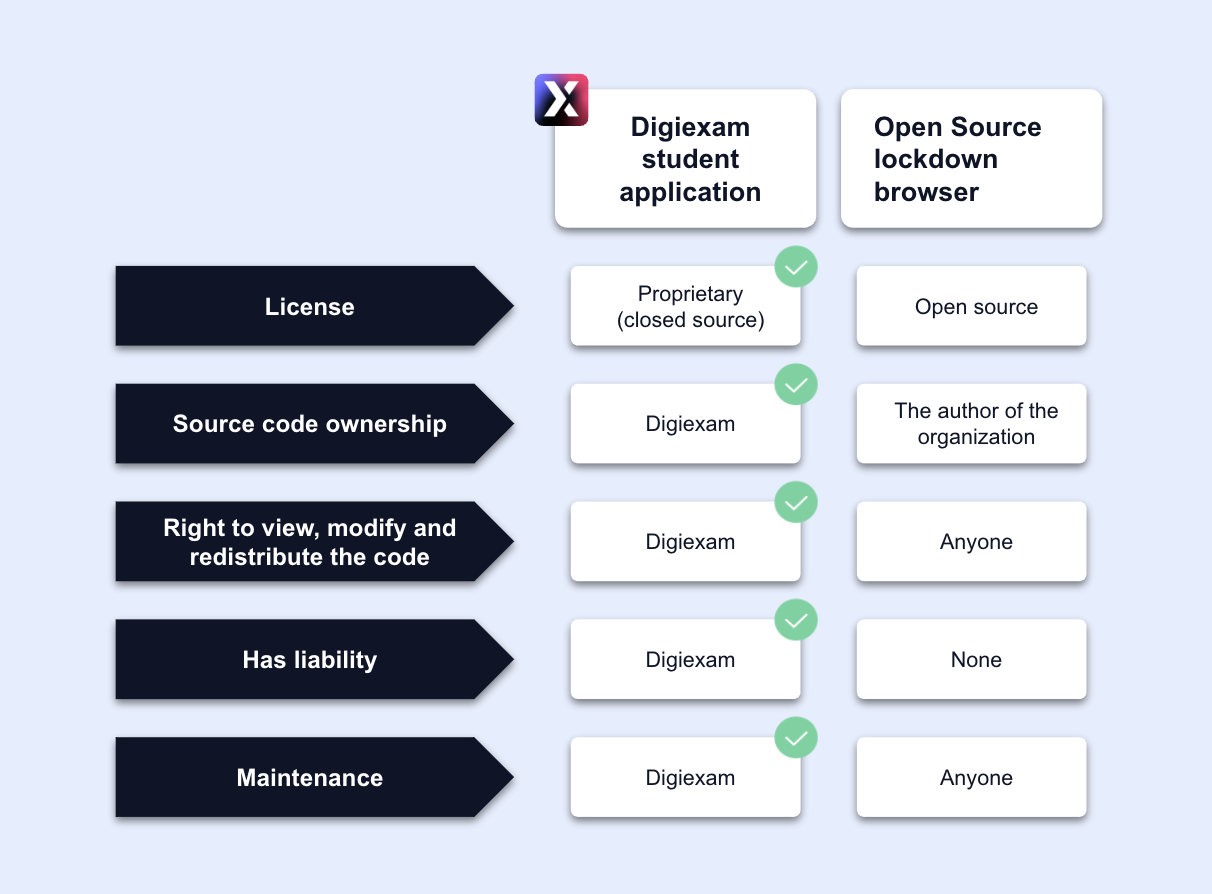
License:
- Digiexam: We are independent and own our source code, hence we can enforce a higher level of security.
- Open Source lockdown browser: Anyone can do whatever they want with the exam browser’s source code to modify it according to their wishes.
Ownership:
- Digiexam: We take ownership of our platform, where we are free to use it however we want.
- Open Source lockdown browser: They do not own their technology and are therefore not allowed to change licensing of it freely.
Right to modify:
- Digiexam: Only we have the right to modify the source code.
- Open Source lockdown browser: Everyone has the right to view, modify, and redistribute the code (including students).
Liability:
- Digiexam: We have total liability that our product works as intended.
- Open Source lockdown browser: No one is liable that an open source exam browser works as intended.
Maintenance:
- Digiexam: Maintenance of the source code for the Digiexam platform is done by paid, experienced, and professional developers.
- Open Source lockdown browser: Maintenance of the examination technology is done by volunteers, where many have few, or no, contributions.
.jpg?width=100&name=TW0_5573%20(1).jpg)
